Deploy a Laravel App to Laravel Forge
Deploy a Laravel app with an encrypted .env.vault file to Laravel Forge.
Find a complete code example on GitHub for this guide.
Initial setup
Install Laravel and create a new Laravel project.
composer create-project laravel/laravel yourapp
Edit resources/views/welcome.blade.php.
resources/views/welcome.blade.php
Hello {{ env('HELLO') }}.
Commit that to code and push it up to GitHub.
git commit -am "Initial setup"
git push
Next, create your project on Laravel Forge.
Laravel Forge Setup
Connect your provider (if you haven't already done so). Here, I am connecting Digital Ocean.
Next, go to the servers page and click Create Server.
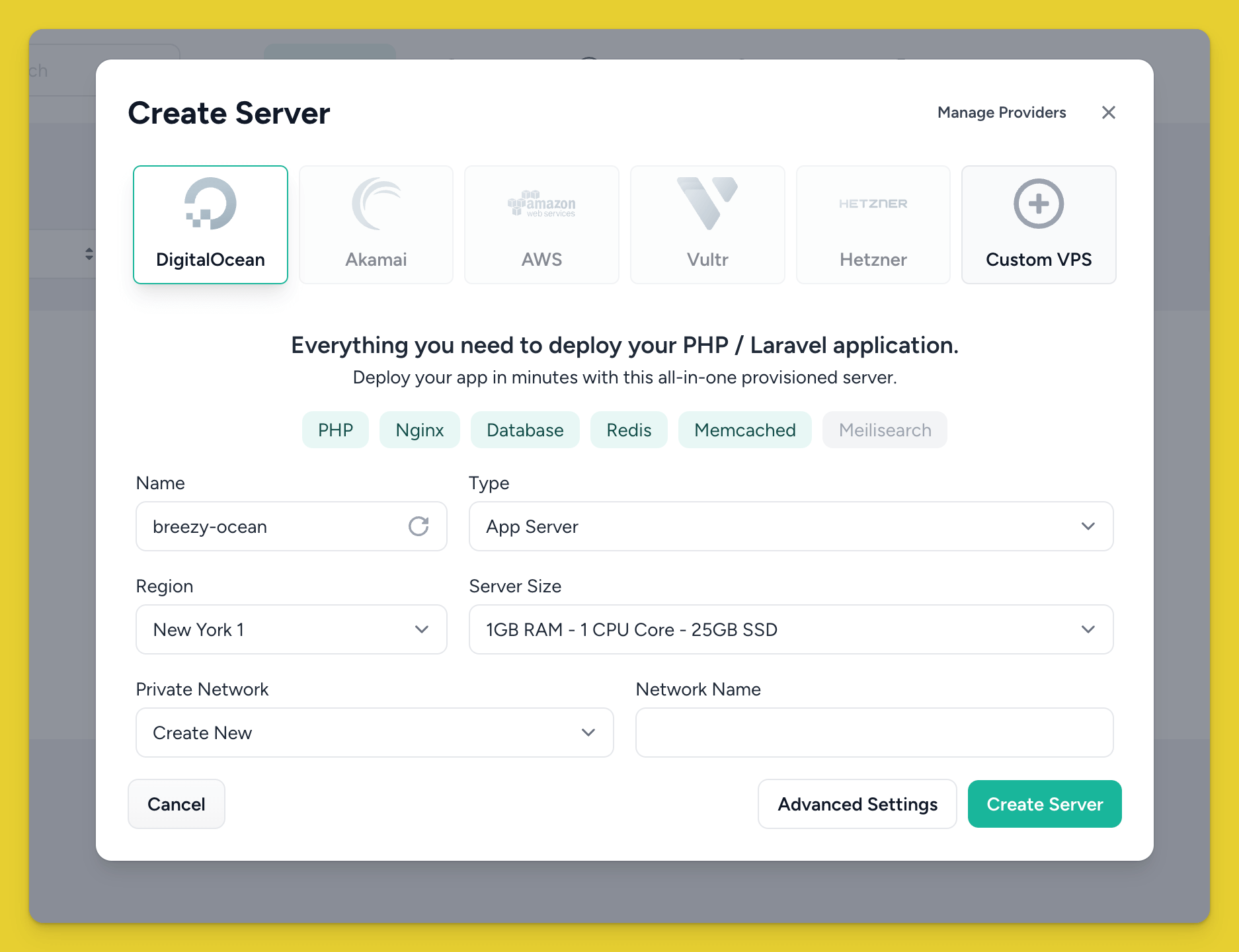
Laravel Forge will bootstrap that server with everything it needs. Give it a few minutes to complete.

Lastly, connect that server to your Laravel application on GitHub.
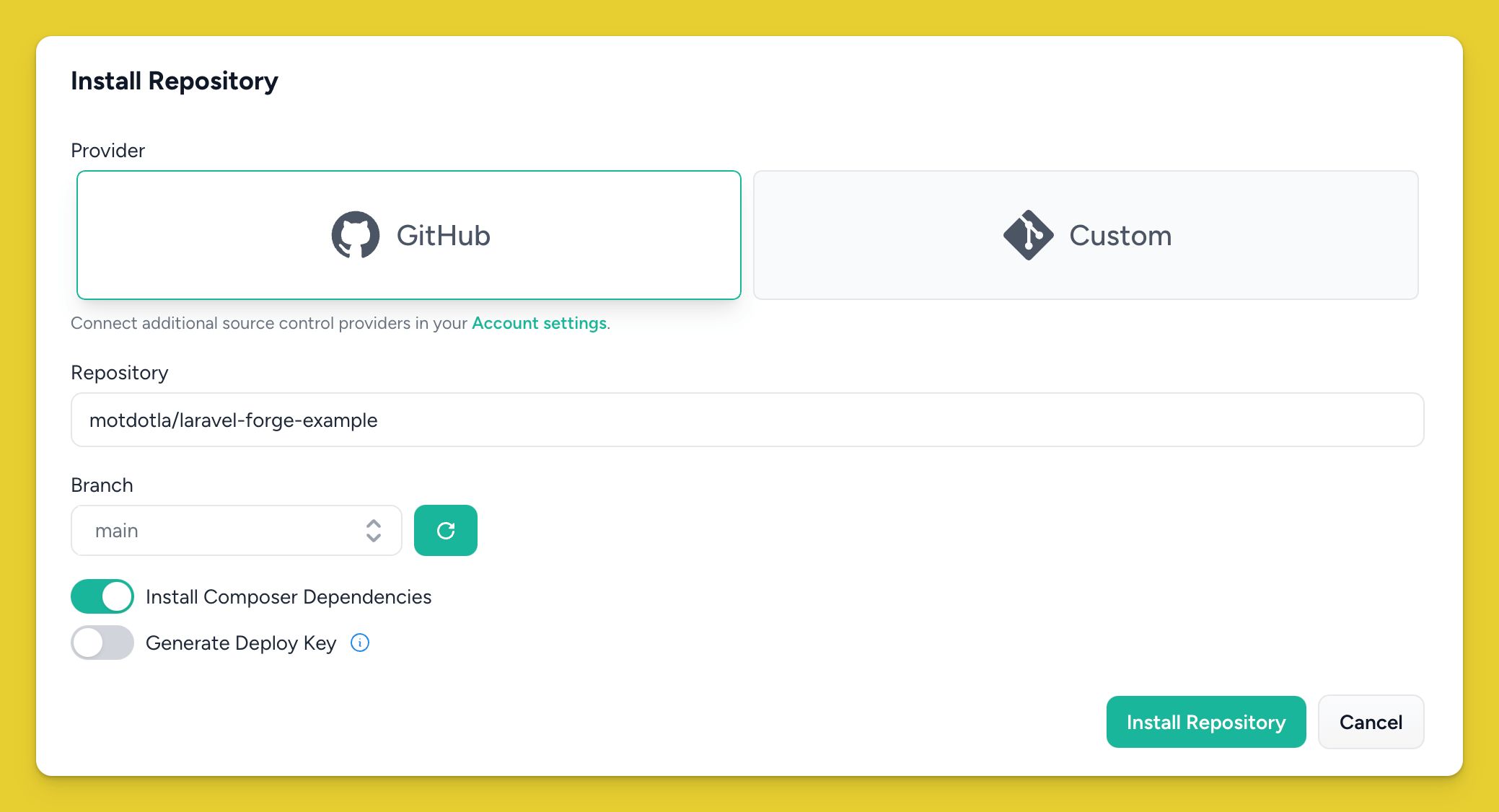
Click Install Repository. Laravel Forge will install your application to your server. This takes a few minutes, and you might have to refresh the page.
Next, go to your application's dashboard and click Deploy Now.
Once the deploy is finished, you can visit the ip address of your server. (I couldn't find this in Laravel Forge's dashboard. I had to go to Digital Ocean and view the droplet.)
Your browser might warn you that the ip address is dangerous, but you can skip that and go straight to it.
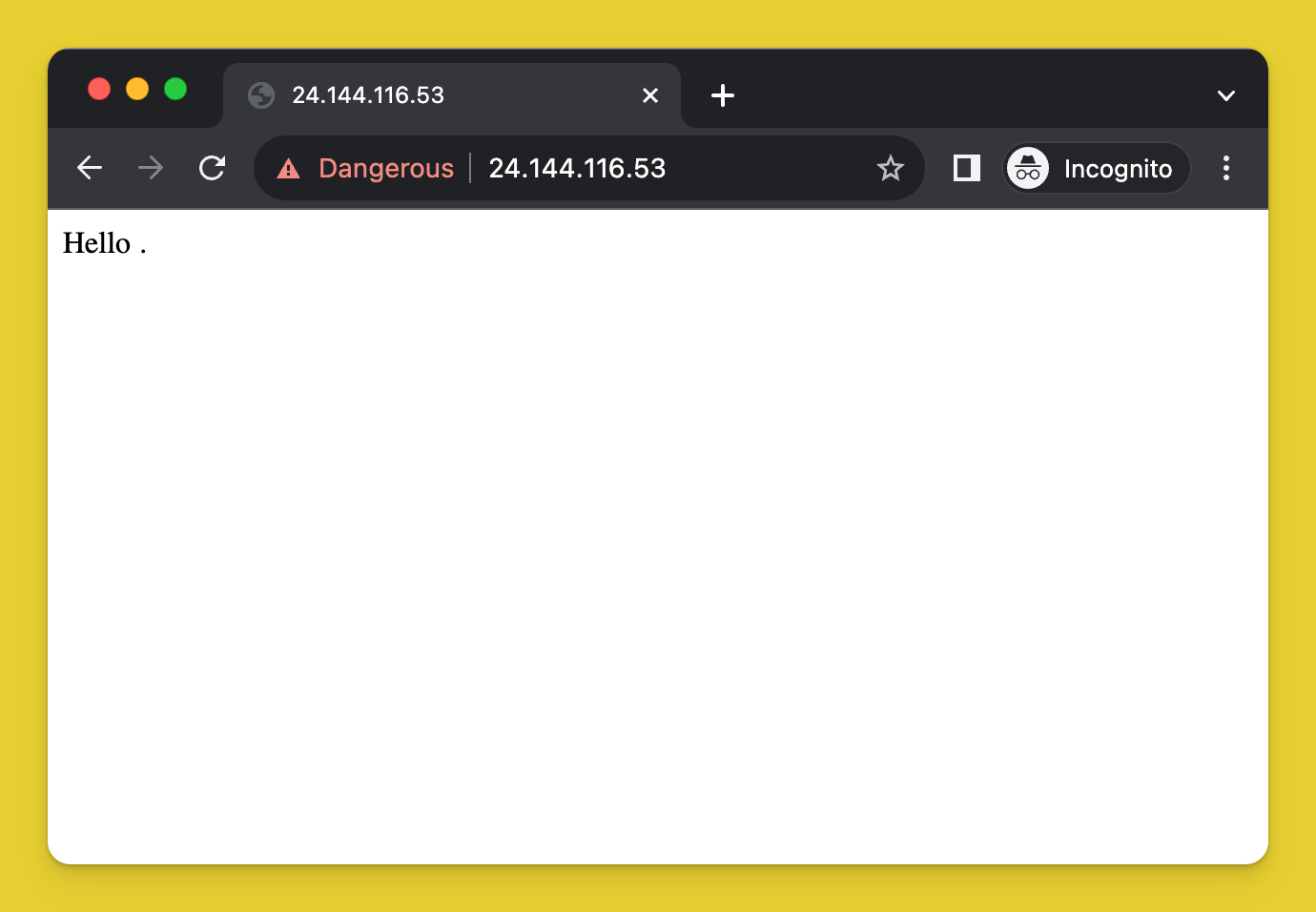
Your app will say 'Hello .' as it doesn't have a way to access the environment variable yet. Let's do that next.
Install dotenv-vault-laravel
Require dotenv-vault-laravel in your composer.json file.
composer require davidcochrum/dotenv-vault-laravel
composer.json
...
"require": {
"davidcochrum/dotenv-vault-laravel": "^1.1",
...
}
...
Add HELLO=World to the bottom of your .env file.
.env
...
HELLO="World"
Try running it locally.
php artisan serve
INFO Server running on [http://127.0.0.1:8000]
It should say Hello World.
Great! ENV now has the keys and values you defined in your .env file. That covers local development. Let's solve for production next.
Build .env.vault
Push your latest .env file changes and edit your production secrets. Learn more about syncing .env files
npx dotenv-vault@latest new
npx dotenv-vault@latest push
npx dotenv-vault@latest open production
Set all those secrets to match the secrets you have in Laravel Forge.
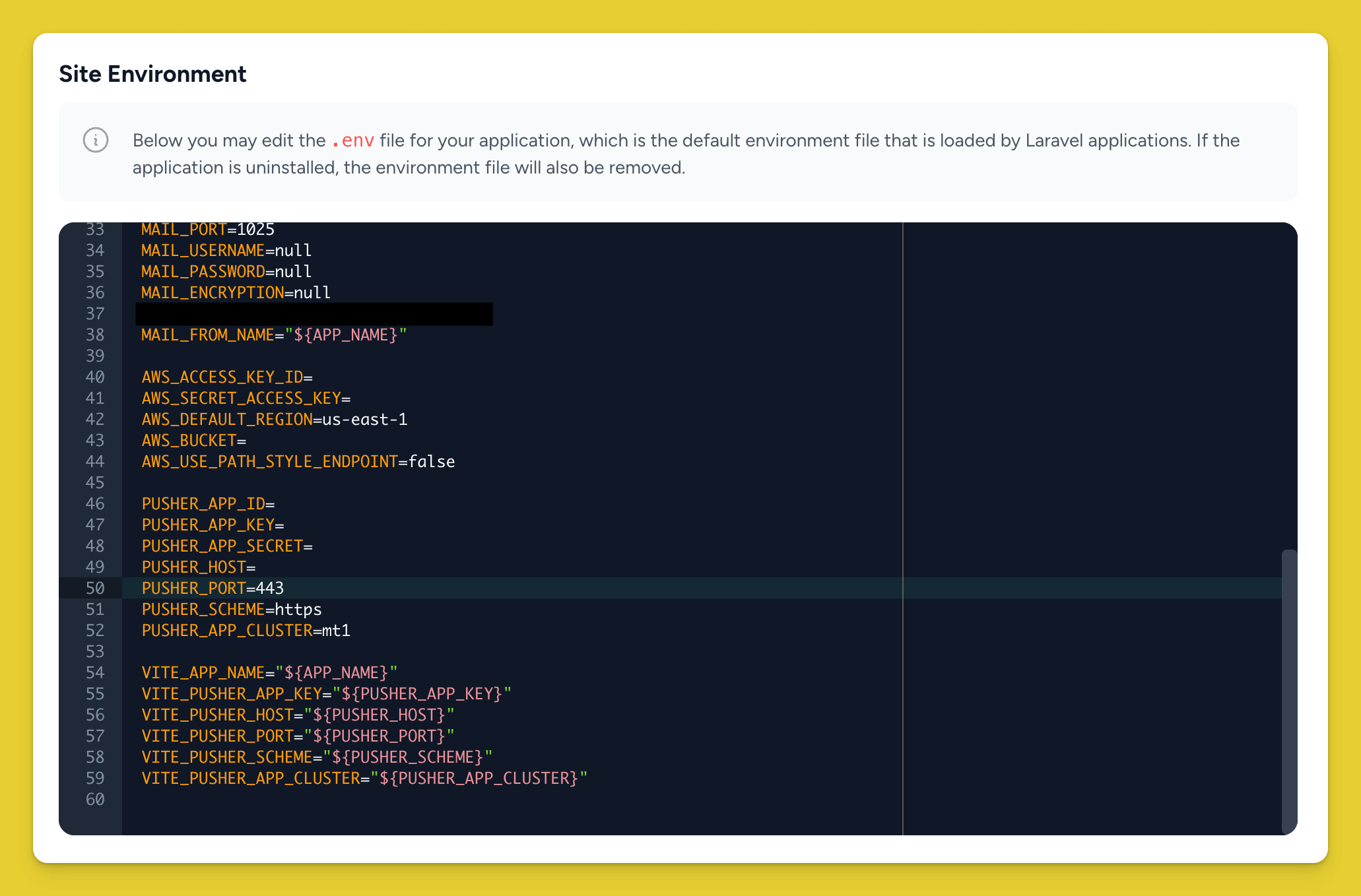
Use the full edit mode feature to paste in all the contents at once.
Lastly, add the secret HELLO. Set the value to production.
Then build your encrypted .env.vault file.
npx dotenv-vault@latest build
Its contents should look something like this.
.env.vault
#/-------------------.env.vault---------------------/
#/ cloud-agnostic vaulting standard /
#/ [how it works](https://dotenv.org/env-vault) /
#/--------------------------------------------------/
# development
DOTENV_VAULT_DEVELOPMENT="/HqNgQWsf6Oh6XB9pI/CGkdgCe6d4/vWZHgP50RRoDTzkzPQk/xOaQs="
DOTENV_VAULT_DEVELOPMENT_VERSION=2
# production
DOTENV_VAULT_PRODUCTION="x26PuIKQ/xZ5eKrYomKngM+dO/9v1vxhwslE/zjHdg3l+H6q6PheB5GVDVIbZg=="
DOTENV_VAULT_PRODUCTION_VERSION=2
Set DOTENV_KEY
Fetch your production DOTENV_KEY.
npx dotenv-vault@latest keys production
# outputs: dotenv://:[email protected]/vault/.env.vault?environment=production
Set DOTENV_KEY on Laravel Forge using the UI.
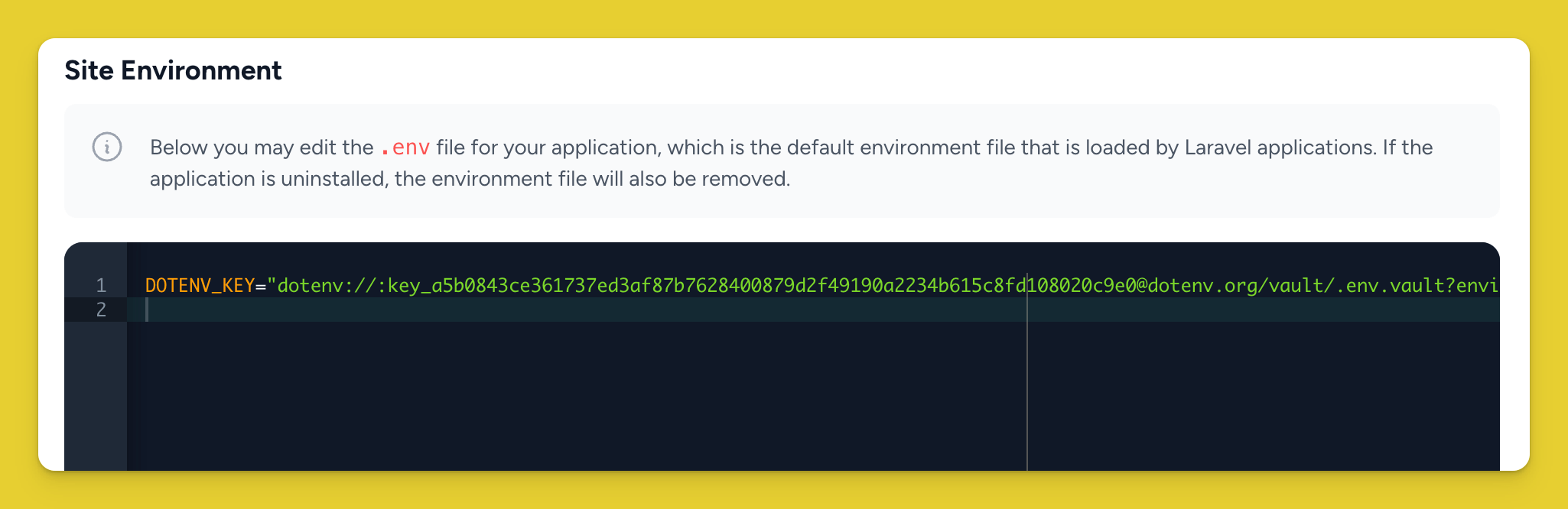
You can remove all the other environment variables as those are now living in an encrypted fashion in your .env.vault file.
Deploy
Commit those changes safely to code and deploy.
That's it! On deploy, your .env.vault file will be decrypted and its production secrets injected as environment variables‚ just in time.
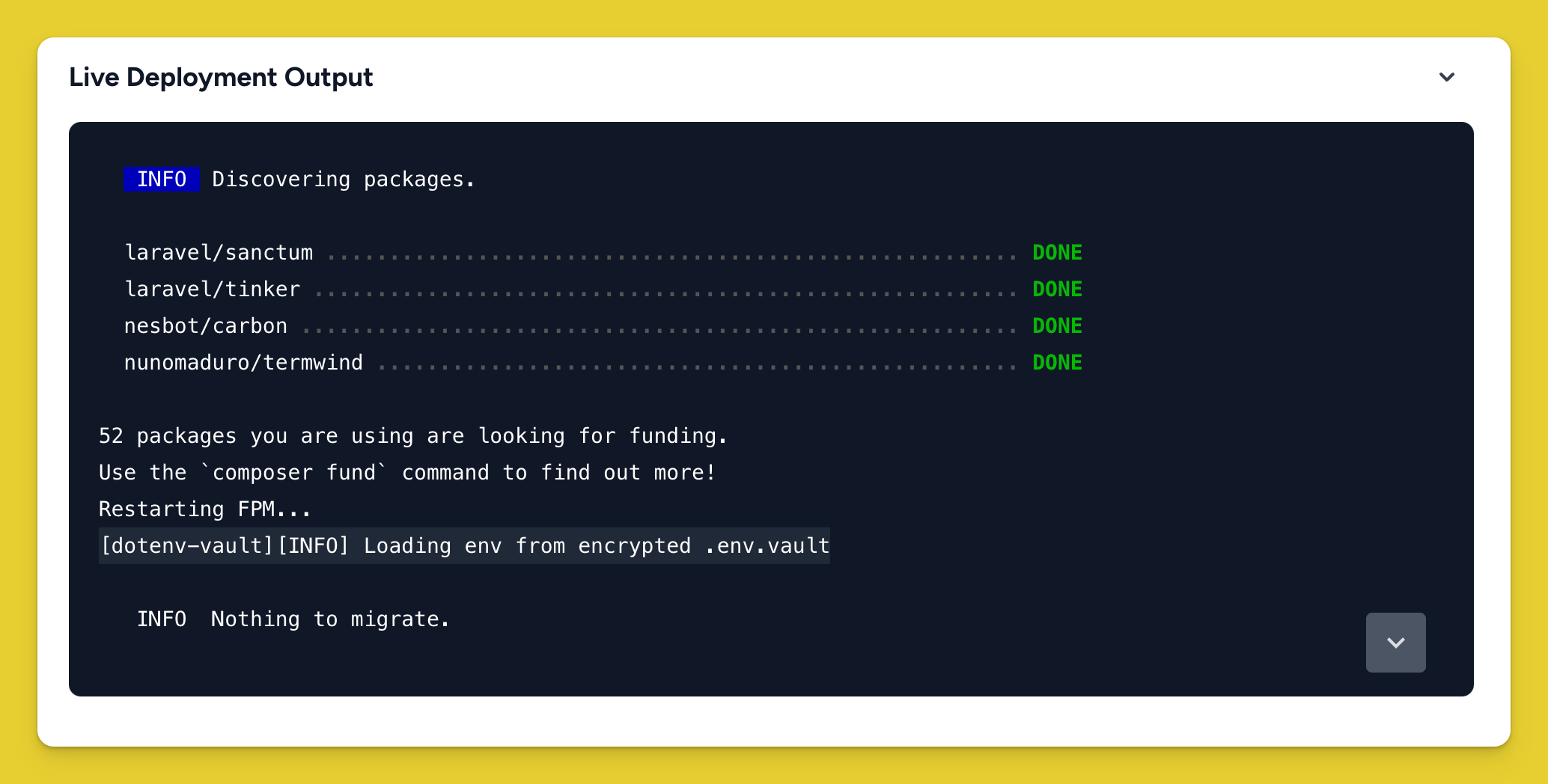
You'll know things worked correctly when you see Loading env from encrypted .env.vault in your logs. If a DOTENV_KEY is not set (for example when developing on your local machine) it will fall back to standard phpdotenv functionality.
You succesfully used the new .env.vault standard to encrypt and deploy your secrets. This is much safer than scattering your secrets across multiple third-party platforms and tools. Whenever you need to add or change a secret, just rebuild your .env.vault file and redeploy.